Mechanical engineering is one of the most general and flexible fields of engineering. It deals with the design, analysis, production, and upkeep of mechanical systems. Mechanical engineering is the field that powers industries like aerospace, automotive, energy, and robotics.
Mechanical engineers are very important in shaping the world around us. They work on things like making robots that are at the cutting edge and cars that use less energy.
Key Takeaways:
- This complete article explains the basic ideas of mechanical engineering, which helps students understand how it affects fields like robotics, aircraft, and renewable energy.
- Readers will learn important skills that are necessary for success in this field, such as how to use CAD, how to understand thermodynamics, and how to think critically to solve problems.
- This article gives a full, step-by-step guide on how to become a mechanical engineer, including the degrees, internships, and hands-on training you need.
- Students look into new job openings in the field that are being created by new technologies like AI integration, nanotechnology, and sustainable manufacturing.
- This article talks about different job duties and career paths, helping people who want to work in both the public and private sectors connect what they learn in school to real-life job opportunities.
What Do Mechanical Engineers Do?
A lot of people want to know what a mechanical engineer does. Mechanical engineers use physics, math, and material science to make machines and systems that make our lives better. They work in many fields, such as aerospace, automotive, energy, robotics, and healthcare. Some of the things they do a lot are:
- Creating and testing machines and systems that work.
- Creating new ways to make things more efficient.
- Doing research on energy sources and materials.
- Making machines work better and encouraging sustainability.
- Finding and fixing problems in mechanical systems.
- Watching over the production and upkeep of machines and tools.
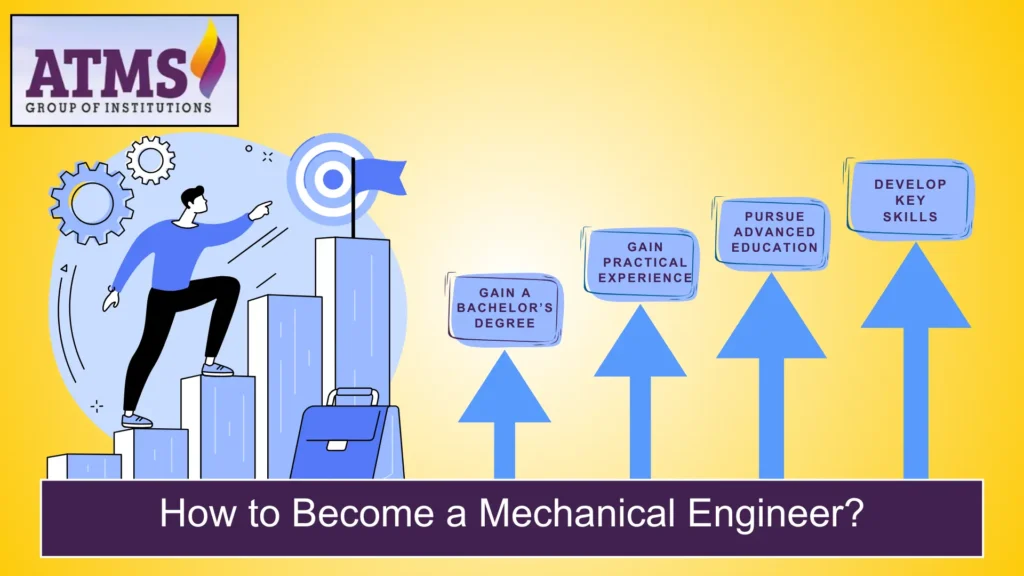
How to Become a Mechanical Engineer?
Wondering what it takes to be a mechanical engineer? The first step is to get an education and some experience. Follow these steps:
- Learn Important Skills – To be successful, you need to be good at problem-solving, being imaginative, skilled in engaging with others, and analyzing things. What does a mechanical engineer know how to do? They include being good at CAD (Computer-Aided Design), knowing about thermodynamics, and being an expert in machine design.
- Get a bachelor’s degree. You need a degree in mechanical engineering or a related field. There are many universities that offer programs in mechanical engineering technology and other areas of study. What kind of degree do you need to work as a mechanical engineer? The most common way to get there is to get a Bachelor in Technology in Mechanical Engineering (B-Tech).
- Get Real-World Experience: Internships and cooperative education (co-op) programs let you learn by doing. A lot of students want to know what kind of training they need to become a mechanical engineer. Internships and lab work are usually part of this training.
- Optional: Get More Education – With a master’s or doctoral degree, you can focus on fields like robotics or aerospace engineering. What are the different master’s degree options in mechanical engineering? Mechatronics, materials engineering, and thermal sciences are all great fields to study.
Essential Skills for Mechanical Engineers
People who want to be successful in mechanical engineering need to learn a lot of skills. These are:
- Technical Skills: You should be good at CAD (computer-aided design), thermodynamics, mechanics, and robotics.
- Problem-Solving: Being able to figure out what’s wrong with a complicated mechanical problem and fix it.
- Creativity: Coming up with new and useful engineering solutions.
- Communication: Being able to explain technical ideas clearly to teams and stakeholders.
- Mathematical Aptitude: A solid understanding of calculus, physics, and statistics.
- Project management is the art of organizing tasks, managing resources, and getting things done on time.
- Adaptability and Continuous Learning: To stay competitive in the field, you need to keep up with new trends, technologies, and industry developments.
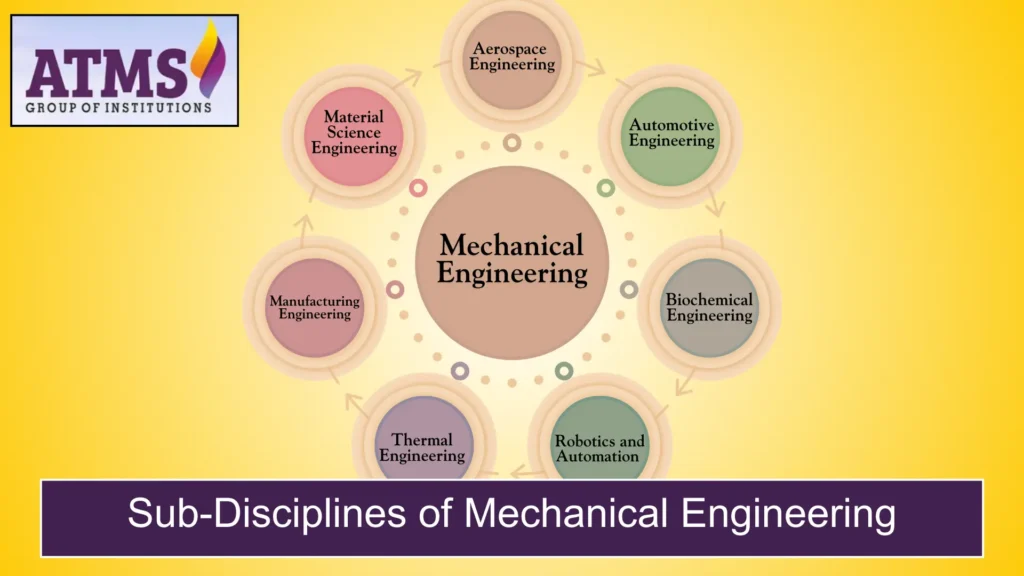
Sub-Disciplines of Mechanical Engineering
There are many areas of specialization within mechanical engineering, such as:
- Aerospace Engineering is the field that deals with the design and development of aircraft, spacecraft, and defense technologies.
- Automotive Engineering: Making cars safer, better at what they do, and more environmentally friendly.
- Biomechanical Engineering is the use of engineering principles to medical devices and the way people move.
- Robotics and Automation: Making robots and technologies that automate tasks.
- Thermal Engineering is the study of how heat moves, how energy systems work, and how HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) works.
- Manufacturing Engineering is the study of production processes, machinery, and quality control.
- Material Science Engineering is the study of the properties and uses of materials in different fields.
Future of Mechanical Engineering
The future of mechanical engineering is exciting because new technologies are making new things possible. A lot of people want to know what you can do with a degree in mechanical engineering. The answer is new ideas. Here are some new trends that will affect the future of mechanical engineering:
- AI and machine learning are changing the way mechanical systems work and how things are made.
- Sustainable Engineering: Focus on eco-friendly options like renewable energy and green manufacturing.
- 3D printing and additive manufacturing are changing how products are designed and how quickly prototypes are made.
- Smart Materials and Nanotechnology—making materials that can heal themselves and remember their shape.
- Space Exploration: Mechanical engineers are very important to missions to space and to exploring other planets.
- Advanced Robotics: The use of robots in many fields, from healthcare to manufacturing, will make things more efficient and lighten the load on workers.
- Quantum Computing Applications – Quantum computing advancements in simulations and material discoveries will help mechanical engineering.
- Renewable Energy and Hydrogen Technologies—Using hydrogen as a clean energy source and making wind, solar, and geothermal power even better will help the environment.
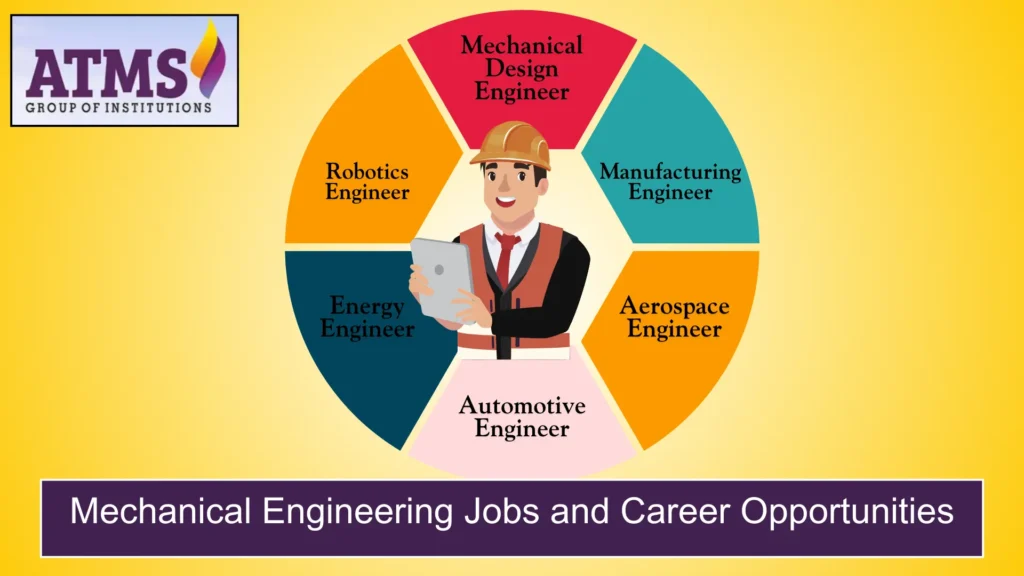
Mechanical Engineering Jobs and Career Opportunities
People often ask, “What do mechanical engineers do?” There are many different jobs in Mechanical Engineering for mechanical engineers in many different fields. Some common jobs are:
- Mechanical Design Engineer: Making plans for machines and mechanical systems.
- Manufacturing Engineer: Making production processes better and more efficient.
- Aerospace Engineer: Works on technologies for aircraft, spacecraft, and defense.
- Automotive Engineer: Making cars safer, better at what they do, and better at what they do.
- Energy Engineer: Making energy solutions that are long-lasting and renewable.
- Robotics Engineer: Creating new ways to use automation and robotics.
- HVAC Engineer: Designing and improving systems for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
- Biomedical Engineer: Making medical devices and prosthetics to make healthcare better.
- Marine Engineer: Designing and keeping ships, submarines, and structures on the ocean in good shape.
- Nuclear Engineer: Works on building and keeping up nuclear reactors and energy systems.
- Materials Engineer: This job focuses on the properties of materials and how they can be used in different fields.
- Maintenance Engineer: Making sure that machines and mechanical systems work well and safely.
- Consulting Engineer: Giving businesses and organizations expert advice and solutions in mechanical engineering.
- Mechatronics Engineer: Someone who designs smart systems by combining mechanical, electrical, and software engineering.
Mechanical engineering also leads to jobs in management and leadership, like Project Manager, Engineering Manager, and Chief Technical Officer (CTO) at companies that are working on the latest technologies.
Conclusion
Mechanical engineering is a field that is always changing and has endless possibilities. This field offers a rewarding and meaningful career whether you want to design cutting-edge technology, improve manufacturing processes, or come up with ways to use renewable energy.
You can make a real difference in the world and drive innovation if you have the right education, skills, and hands-on experience. There are many things you can do with a degree in mechanical engineering if you’ve ever wondered what to do with it.
Mechanical engineering is a key part of modern innovation in many fields, including aerospace, automotive, biomedical, robotics, and even energy solutions.