You just finished 12th grade and are now thinking about what to do next. What course should you take for your higher studies?
You probably chose to study engineering because you want to build things, solve problems, or make a real difference in the world. But now you’re confused and probably asking yourself, “What is engineering?”
And why is it so important? There are a lot of different kinds of engineering, which can be overwhelming. Don’t worry, we’ve made it easier for you.
First, picture a world where the lights never turn on, you can only get around by walking or riding a bike, diseases spread without control because there isn’t enough medical technology, and you can only talk to people by shouting over long distances. That’s how the world would be if there were no engineering.
This article is about “What is Engineering?” We will look into the idea of what engineering is and how it is changing and affecting the world.
The different kinds of engineering, where they are used in different fields or industries, and the jobs you can get in those fields of engineering. We will also talk about new areas of engineering that are starting to grow, the future of engineering, and how to become an engineer.
Key Takeaways:
- This article uses real-life examples to help students understand what engineering is and how it affects their daily lives.
- Readers can learn a lot about the main fields of engineering, such as mechanical, civil, electrical, and computer science.
- The article talks about new technologies like AI, renewable energy, and space technology that inspire young people to study futuristic engineering.
- Students can follow step-by-step instructions to start their engineering journey with clear information on how to become an engineer.
- The article shows how engineering education can lead to real jobs, helping students connect what they learn in school to job opportunities in their area and around the world.
What is Engineering? A Simple Explanation
Engineering is the use of science, math, and creativity to design, build, and improve systems, processes, machines, and structures.
It is all about finding practical and useful ways to solve problems in the real world. To make things like bridges, software, medical devices, and clean energy systems that make life better, engineers need to be creative and able to think critically.
Key Aspects of Engineering:
- Problem-Solving: Engineering can help solve a lot of problems in the world, from small ones to big ones.
- Innovation: Engineering is at the cutting edge of new technologies, making things like self-driving cars and AI possible.
- Mathematics and Science: These are the most important parts of engineering because they make sure that solutions work and are safe.
- Practical Applications: Engineering turns what we know about theory into real-world benefits for people.

The Impact of Engineering in Everyday Life
Now you might have a better idea of what engineering is. Let’s look at how it has changed our daily lives and how it is very important to the things we do every day.
Transportation and Infrastructure:
Civil engineering is the answer to all of our infrastructure and transportation needs. It designs roads, bridges, and skyscrapers, including the amazing Burj Khalifa.
Mechanical engineering is taking automotive technology to new heights, especially with new ideas like electric cars and self-driving Autopilot systems.
Communication & Technology:
Electrical and software engineering have given us smartphones, the internet, and cloud technology. These things have completely changed how we connect with others and get things done every day.
Healthcare and Medicine:
Biomedical engineering has changed medical care forever by giving us MRI machines, prosthetics, and even genetic engineering methods.
Renewable Energy & Environment:
Engineers make solar panels, wind turbines, and smart grids, which are all steps toward a cleaner, greener future.
Specific Examples of modern engineering
Let’s look at some examples of engineering that use different fields of engineering to make amazing things that show how our society has changed in terms of technology and infrastructure.
The Burj Khalifa in Dubai is not only the tallest building in the world, but it is also a symbol of great civil engineering because it looks good and works well.
The Electric Vehicles Autopilot system shows how electrical and software engineering can work together with AI to make driving safer.
The International Space Station is a great example of modern engineering. It shows how different fields of engineering, like mechanical, electrical, aerospace, and computer engineering, can work together to make it possible for people to live and work in space and do groundbreaking research.
Engineering and its Types?
You should know by now what engineering is and how it affects daily life. You probably want to learn more about this field, but you might be wondering what kind of engineering branch you should study. Don’t worry; we’ve got your back.
Engineers can work in many different fields and solve many different kinds of problems because each branch of engineering focuses on a different area of study and application. This variety in engineering lets students and professionals pick a path that fits their skills and interests.
We will look at some of the main branches of engineering, how they are used in the real world, and the jobs you can get in the field of engineering that interests you.
Mechanical engineering:
Mechanical engineering is the field of engineering that deals with making, fixing, and using machines. It includes everything from engines and cars to tools, robots, and manufacturing systems.
Uses: Designing engines, making robots, HVAC systems, manufacturing processes, and transportation systems.
Job options include automotive engineer, robotics engineer, aerospace engineer, manufacturing engineer, and design engineer.
Learn more about Mechanical Engineering by reading our latest article on What is Mechanical Engineering?
Electrical Engineering:
Electrical engineering is mostly about the large-scale generation, transmission, distribution, and use of electric power and electric systems.
Uses: making power, sending and distributing it, electric machines, control systems, and electricity infrastructure. Electrical engineer, power systems engineer, renewable energy engineer, and telecommunications engineer are all jobs that you can get.
Learn more about Electrical Engineering by reading our latest article on The Ultimate Guide to Electrical Engineering: Scope, Careers & Future Trends
Electronics Engineering:
This branch of engineering is responsible for designing, developing, and testing small electrical parts such as chips, circuits, electronic devices, and digital systems.
Uses: consumer electronics, electronic circuits and components, microprocessors and microcontrollers, communication systems, and embedded systems.
Job Options: Embedded System Engineer, Electronics Engineer, Control System Engineer, Telecommunication Engineer, and VLSI Design Engineer
Learn more about Electronics Engineering by reading our latest article on The Ultimate Guide to Electronics Engineering: Scope, Careers & Future Trends
Civil Engineering:
Civil engineering is the field that deals with planning, building, and keeping up with infrastructure. Civil engineers use science and math to build and keep things like roads, bridges, tunnels, dams, and buildings in good shape.
Applications: Designing and building smart and strong infrastructure, bridges, dams, and tunnels.
You could work as a site engineer, structural engineer, environmental engineer, transportation engineer, or geotechnical engineer.
Learn more about Civil engineering by reading our latest article on What is Civil Engineering?
Computer Science Engineering:
Computer Science Engineering is the study of computers, algorithms, data structures, and the ideas behind how computers work.
This kind of engineering uses math and logic to come up with new technologies and solve hard problems. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Data Science, Cyber Security, Operating Systems, and Research and Innovation in Algorithms and Computation are all examples of applications.
There are jobs available as an Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Engineer, Data Scientist, Cyber Security Analyst, or Cloud Engineer.
Learn more about Computer Science Engineering by reading our latest article on Computer Science- Definition, Applications, Career and Jobs
Software Engineering:
Software Engineering is a type of engineering that is similar to Computer Science Engineering in some ways but is its own thing. It involves creating, designing, testing, and keeping up reliable and useful software systems that solve real-world problems, often building on what computer science engineering has already done.
Applications: Making apps for phones and computers, making websites and web apps, Making and testing big software systems, Keeping cloud-based apps up and running and growing Software Developer, Frontend/Backend Developer, DevOps Engineer, Full Stack Developer, Mobile App Developer, and SaaS Engineer are some of the jobs you can get.
Aerospace Engineering:
This branch of engineering deals with the design, development, and upkeep of aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and rockets. It is a specific type of engineering that combines different fields to learn about the science behind aerospace technology.
Uses: Making planes, satellites, rockets, vehicles for exploring space, and making aviation safer and better.
Job Options: Aerospace Engineer, Avionics Engineer, Satellite Engineer, and Flight Test Engineer.
Chemical Engineering:
Chemical engineering is the part of engineering that deals with using chemical processes to design and make raw materials into useful products. It focuses on the design process to make things like food, fuel, medicine, plastics, clean water, and more.
Uses: Making medicines, fertilizers, and agrochemicals; cleaning water; processing oil and fuel; and more.
There are many jobs you could get, such as process engineer, pharmaceutical engineer, quality control analyst, petrochemical engineer, or research scientist.
Biomedical Engineering:
Biomedical Engineering (BME) is a field of engineering that focuses on making healthcare better by using biology, medicine, and technology to create medical equipment, devices, and software that help with diagnosing, treating, and improving the health of people and animals.
Medical devices, artificial organs and implants, wearable health tech, biomedical software, and robotic surgery are all examples of applications.
There are jobs available as a medical device engineer, clinical engineer, R&D engineer, or rehabilitation engineer. There are always new and exciting fields of engineering that go beyond the traditional ones.
These include artificial intelligence, nanotechnology, renewable energy engineering, and quantum computing.
These cutting-edge fields have a lot of potential to solve problems around the world and lead to new ideas in the future.
Cutting-Edge: Emerging Fields in Engineering
Now that we know what engineering is, it’s only fair to keep you up to date on the exciting and fast-growing fields that are shaping the future.
These new fields aren’t just passing fads; they’re changing whole industries, opening up new job opportunities, and helping to solve some of the world’s biggest problems.
Let’s take a quick look at some of these new fields that are starting to show up.
AI/ML Engineering:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning AI/ML Engineering uses AI to make manufacturing processes better, make predictive maintenance better, and even build systems that can learn from data to get better over time.
For instance, deep learning algorithms are being made to read medical images and find diseases earlier in their development.
Nanotechnology Engineering:
Nanotechnology is the science of building new materials and devices with unique properties by working with molecules and atoms.
Nanomaterials are being used in medicine to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells while minimizing side effects. This is a big part of this field.
Renewable Energy Engineering:
As the world deals with climate change and the need to protect the environment, renewable energy engineering is changing quickly.
These new ideas in solar, wind, and geothermal technologies are just the start. Engineers are now working on making energy storage systems better, like advanced battery systems, to deal with the fact that renewable energy is always available.
Quantum Computing:
Quantum computing changes the way computers handle data in a big way. Instead of bits, quantum computers use qubits as their smallest unit of data.
Because of the principles of superposition and entanglement, qubits can be in more than one state at once. Quantum computers could use this power to solve problems that can’t be solved now, like finding new drugs by figuring out how molecules interact, breaking cryptographic codes, or optimizing complex systems.
Each of these new fields could have a big effect on many industries, such as healthcare, energy, transportation, and cybersecurity. They also come with new technical challenges. If you dig deeper into these areas, you might find exciting job opportunities and new ideas that will change the way we live.
How to Become an Engineer?
We talked about what engineering is, how it changes the world, the different kinds of engineering, and the new fields of engineering that are popping up that will change our future.
Let’s move on to something else that’s just as important: how to get a job as an engineer.
A student must do a few things to become an engineer. From choosing the right subject in school to passing the entrance exams and choosing the right college. This is a guide that will help you get started on your engineering journey.
STEM education is important: To be an engineer, you need to know a lot about science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). Taking hard classes and joining clubs or science fairs outside of school can help you learn even more and get better at these subjects.
Get a bachelor’s degree: Most entry-level engineering jobs require at least a bachelor’s degree in engineering. Pick a major that fits your interests and career goals, like civil, computer, or software engineering, for example.
Internships, co-op programs, and personal projects are all great ways to get real-world experience that will help you learn the skills that employers want. You can also learn about different fields of engineering and what you like through these experiences.
If you want to learn more advanced things, you might want to go back to school. If you have a master’s or doctoral degree (Ph.D.), you can work in engineering and do research.
Taking advanced classes can also help you stay ahead in this field, which is changing quickly.
You will always be learning. Engineering is always getting new tools and better ways to do things. You can learn new things and stay up to date with the latest trends by going to conferences, workshops, and online courses.
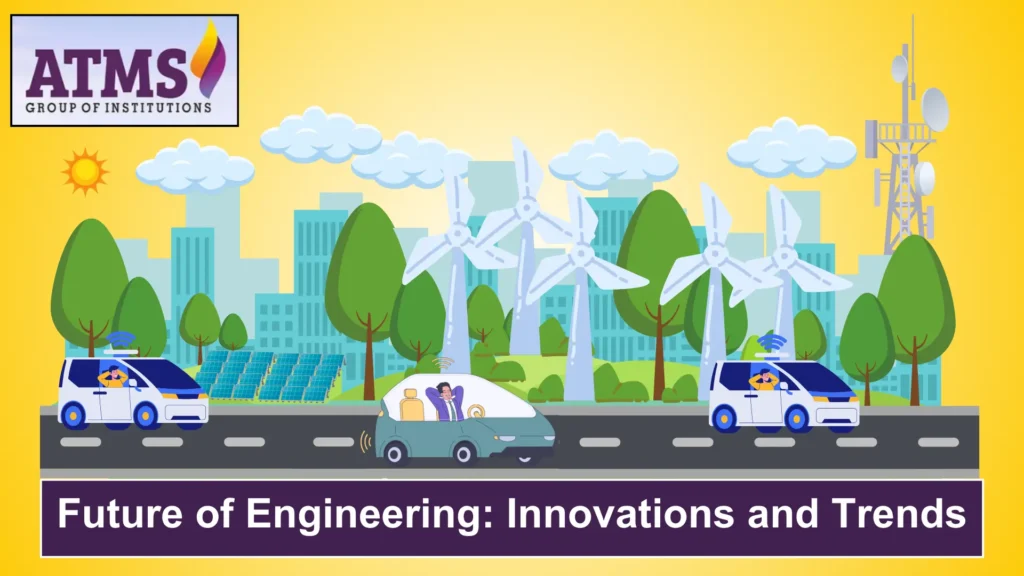
The Future of Engineering: Innovations and Trends
If we look around us, we can see that the definition of engineering will change a lot over time. This is because technology and tech education are always changing.
Let’s see how this goes, and we can say that engineering is on the verge of another revolution. Some common examples are:
Self-Driving Cars: Changing the way we get around by making it safer and more efficient.
AI in Healthcare: AI is going to save lives by helping with everything from diagnosis to personalized medicine.
Sustainable Urban Development: Making cities that are smart, eco-friendly, and high-tech.
Space Exploration: The next big thing, with private companies like SpaceX leading the way to travel between planets.
Conclusion
There it is, we’ve learned what engineering really is. It’s more than just a profession; it’s a driving force behind human progress and innovation. From the ancient pyramids to modern marvels like artificial intelligence and quantum computing, engineering and engineers have played a pivotal role in shaping our world.
As we face new challenges and opportunities in the 21st century, engineering offers a demanding yet rewarding career path for those who are passionate about innovating and making a positive impact on the world. If you’re curious about how things work, passionate about problem-solving, and eager to make a difference, a future in engineering might be waiting for you.
So if you’re still wondering ” what is engineering” just look around and you’ll see how it is shaping our future. Whether it is self-driving cars, artificial intelligence or clean energy, you can see how engineering is building tomorrow’s today. The question is – are you ready to become an engineer?
I will immediately take hold of your rss as I can not
in finding your e-mail subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service.
Do you have any? Kindly let me recognize so that I may just subscribe.
Thanks.
Yes we do have a newsletter, please share your email Id here!