Learn about civil engineering, its past, its different parts, and the jobs you can get in this field. This complete guide will tell you what civil engineers do, how to become one, and what courses, degrees, and trends are coming up in the field of civil engineering.
Civil engineering is one of the oldest and most important fields of engineering. It is in charge of planning, building, and keeping up the built environment. Civil engineers build the infrastructure that makes modern life possible, from roads and bridges to skyscrapers and water treatment plants.
But what is civil engineering, and what do civil engineers do? Let’s look into the field, job options, and school options that are available to people who want to become civil engineers.
Key Takeaways:
- This complete guide explores the history and evolution of civil engineering, showing how it has progressed from ancient civilizations like the Indus Valley to modern AI-driven smart cities.
- Readers will gain a clear understanding of what civil engineers actually do, including their critical roles in infrastructure development, structural analysis, and environmental management.
- The article breaks down the major branches of the field—such as Structural, Geotechnical, and Transportation Engineering—helping students identify which specialization aligns with their interests.
- Aspiring engineers will find a detailed roadmap on how to enter the profession, covering essential degrees, technical skills like CAD, and soft skills needed for project management.
- The post highlights future trends and challenges, discussing how sustainable construction, green buildings, and 3D printing are transforming career opportunities in 2026.
History of Civil Engineering
The history of civil engineering is what has made civilizations possible. Civil engineering has been around for thousands of years. For example, the Indus Valley Civilization (2600 BCE) had well-planned streets, reservoirs, and advanced drainage systems in cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro.
The Industrial Revolution led to quick improvements in materials and building methods, which led to the cities we see today. Today, new civil engineers use cutting-edge tools like AI, 3D modeling, and smart materials to build infrastructure that lasts longer and works better.
What Does a Civil Engineer Do?
A lot of people want to know, “What does a civil engineer do?” or “what does a civil engineer do?” The main job of a civil engineer is to plan, design, and supervise construction projects. They are responsible for:
- Infrastructure Development: Building and keeping up roads, bridges, tunnels, and water supply systems.
- Structural analysis makes sure that buildings and other structures can stand up to natural disasters like earthquakes, hurricanes, and tsunamis.
- Environmental management means dealing with pollution control, waste management, and using resources in a way that doesn’t harm the environment.
- Project Management: Making sure that construction projects follow safety rules and stay within budget.
Civil engineers are very important in shaping our world, whether they work for private companies, government agencies, or as civil engineering consultants.
Major Branches of Civil Engineering
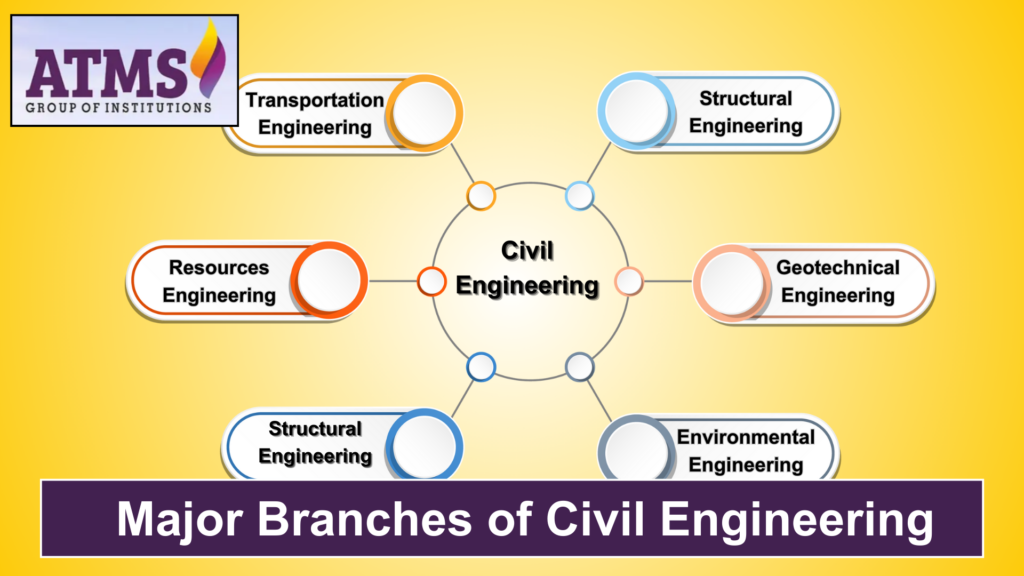
What makes civil engineering such a broad field? There are many different branches of civil engineering, such as:
- Structural Engineering: This field is all about making buildings and bridges that are strong and last a long time.
- Geotechnical engineering is the study of how soil works and how stable foundations are.
- Environmental engineering deals with cleaning up water, controlling air pollution, and getting rid of trash.
- Transportation Engineering: Plans roads, highways, and public transportation systems that work well.
- Water Resources Engineering: Plans and runs projects for water supply, irrigation, and flood control.
- Construction Management: Makes sure that projects are done safely and efficiently.
How to Become a Civil Engineer?

If you’re interested in this field, you might be wondering what civil engineers do and how to become one. The first thing you need to do is get the right education.
How to pursue Civil Engineering
To work in this field, you need at least a bachelor’s degree in civil engineering. A lot of colleges and universities offer civil engineering classes that teach basic subjects like math, physics, and design principles.
A master’s degree in civil engineering is an option for those who want to go even further. It gives you specialized knowledge and chances to do research.
Technical and Soft Skills needed for Civil Engineering
To be successful in the field, aspiring civil engineers need to learn both technical and soft skills in addition to formal education. Some important skills are:
Technical Skills: Knowing how to use CAD software (like AutoCAD and Revit), project management tools, and how to analyze structures and construction materials.
Problem-Solving: The ability to look at tough engineering problems and come up with useful answers.
Communication and teamwork are very important for civil engineers because they work with architects, contractors, and government agencies.
Mathematical and Analytical Skills: You need to have a solid understanding of math, physics, and design principles.
Adaptability and innovation: Staying up to date with new technologies in green building, AI, and smart infrastructure.
To learn useful skills, you need to do internships, apprenticeships, and on-the-job training. Civil engineers can choose to focus on areas like environmental sustainability, transportation, or civil and structural engineering.
Applications in Modern Society

Civil engineers play a role in nearly every part of daily life. Some of the things they do are:
Smart City Development: Building smart infrastructure, like buildings that use less energy and better transportation.
Sustainable Construction: Building green buildings like the Infosys Pune Campus and the ITC Green Center in Gurugram.
Disaster Management: Making buildings that can withstand earthquakes in places like the Himalayas and North-East India that are prone to earthquakes.
Building solar and wind farms like the Pavagada Solar Park in Karnataka and the Kutch Wind Farm in Gujarat is part of renewable energy infrastructure.
As the need for sustainable infrastructure grows, new civil engineers need to focus on coming up with new ideas and thinking about how they will affect the environment in the long term.
Challenges and Future Trends in Civil Engineering

Challenges in Civil Engineering
Civil engineering is very important for building infrastructure, but it has a lot of problems to deal with:
Climate Change and the Future
Infrastructure is in danger from rising global temperatures, unpredictable weather, and rising sea levels. To lower these risks, engineers need to build structures that can withstand floods and are good for the environment.
Infrastructure that is getting old
A lot of countries have problems with their roads, bridges, and water supply systems getting worse. Engineers need to find a balance between the need for repairs and replacements and keeping costs low for the environment and the economy.
Overpopulation and Urbanization
As cities grow quickly, they need good systems for moving people, housing, and trash. It’s getting harder to manage space limits while making sure people are safe and comfortable in crowded areas.
Putting technology together
New technologies like AI, robotics, and automation are changing the industry, but the construction sector has been slower to adopt digital tools than other industries. This has made project management and execution less efficient.
Future Trends in Civil Engineering
- Green and sustainable engineering: People are starting to move toward buildings that don’t use any carbon, designs that are good for the environment, and green roofs. More and more construction companies are using net-zero energy buildings, which make as much energy as they use.
- Integration of Smart Infrastructure and IoT: People are making smart cities with systems that can watch air quality, traffic flow, and the strength of buildings in real time. The Internet of Things (IoT) makes predictive maintenance possible, which lowers the risk of infrastructure failure and makes things work better.
- New Technologies in Construction: 3D printing is changing the way buildings are made by making it possible to build quickly, cheaply, and in a way that is good for the environment. Modular construction is being used to build homes that are faster, bigger, and better for the environment.
- Infrastructure that can handle natural disasters: Engineers are making buildings that can withstand earthquakes, cities that can withstand floods, and structures that can withstand hurricanes. Using materials that are flexible and strong makes sure that they will last even in harsh conditions.
These trends show where civil engineering is headed in the future, making sure that the field keeps changing to meet the needs of today’s society.
Civil Engineering Jobs and Career Opportunities

Civil engineers can work in a lot of different areas, both in the public and private sectors. They can build infrastructure or work as specialized consultants.
- Jobs in the government and public sector Civil engineers are important to projects that build roads, bridges, railways, and cities. A lot of them work for government agencies that are in charge of building, keeping up, and planning for the environment.
- Jobs in the private sector Civil engineers are hired by big construction companies, real estate developers, and infrastructure companies to manage projects, design structures, and oversee sites. Civil engineering skills are also needed in fields like transportation, energy, and water management.
- Consulting and Specialized Positions A lot of civil engineers work as consultants, giving their clients advice on things like transportation planning, environmental engineering, geotechnical studies, and structural analysis. Their skills are very important for making infrastructure that is safe and works well.
- Research and School People with advanced degrees can work in research institutions and universities, focusing on smart infrastructure, disaster resilience, and sustainable building, for example.
- Starting a business and being an entrepreneur New trends in construction technology, green buildings, and modular housing have given civil engineers the chance to start their own businesses or come up with new ideas in the field.
Conclusion
What did civil engineers do in the past, and what do they do now? Civil engineering has changed from old ways of building to new ideas that shape our world. Civil engineers are very important to society because they design bridges, run city infrastructure, and come up with new ways to make things more environmentally friendly.
If you’re thinking about this field, getting a bachelor’s or master’s degree in civil engineering can help you get a good job. Innovation, sustainability, and technology are the keys to the future of civil engineering. This makes it an exciting and important field for the next generation.