Explore the dynamic world of electronics engineering, from integrated circuits and semiconductor technology to embedded systems and IoT. Discover career opportunities, innovative trends, and the future of modern technology.
Electronics engineering is at the heart of the digital revolution, powering everything from consumer devices to advanced computing systems. This discipline involves designing, developing, and testing electronic components and systems that are essential to modern communication, entertainment, healthcare, and beyond.
In this guide, we explore the fundamentals of electronics engineering, dive into diverse career paths, and examine emerging trends that are shaping the future of technology.
What is Electronics Engineering?
Electronics engineering is a branch of electrical engineering that focuses on designing and building electronic circuits, devices, and systems. It includes a wide range of technologies, from microelectronics to digital signal processing, making it necessary for both everyday consumer electronics and complex industrial systems.
Key Areas of Electronics Engineering
- Technology for semiconductors: Engineers in this field design and make semiconductor devices like transistors and diodes, which are the basic parts of microprocessors and integrated circuits.
- Design and Analysis of Circuits: This field includes making electronic circuits that do certain things. To make sure that circuits work, are reliable, and are cost-effective, electronics engineers build and test them.
- Embedded Systems: Embedded systems are specialized computers that combine hardware and software to carry out certain tasks. They are used in many different things, such as home appliances and systems that control cars.
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP): Digital signal processing (DSP) engineers come up with ways and systems to process digital signals. This technology is used in a number of fields, including telecommunications, audio and video processing, and radar systems.
- Communication Systems: Electronics engineers concentrate on the design of systems facilitating both wireless and wired communication, encompassing mobile devices and satellite systems, to ensure efficient and reliable data transmission.

What Do Electronics Engineers Do?
Electronics engineers use ideas from physics, math, and computer science to make electrical devices and systems better and more useful. They work in many different areas, doing both creative design and ongoing testing to make sure things work and are reliable.
Common Tasks of an Electronics Engineer
- Designing and Simulating Electronic Circuits: Engineers create circuit designs and use simulation software to predict how circuits will behave in different situations.
- Designing Microprocessors and Integrated Circuits: They focus on making complex systems smaller and more efficient for modern computing, making sure they work at their best and use the least amount of energy.
- Programming Embedded Systems: Electronics professionals make firmware and software for embedded devices, which makes it possible for things like consumer electronics and automotive systems to work.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Electronic devices go through a lot of testing to make sure they work and are safe. This includes everything from testing individual parts to testing the whole system.
- Research and Innovation: Electronics engineering is based on ongoing research. Engineers look into new materials, ways to make things, and design methods to push the limits of what is possible.
At companies like Intel and AMD, electronics engineers design state-of-the-art microprocessors that power computers and servers, driving the innovation behind faster, more efficient digital devices.
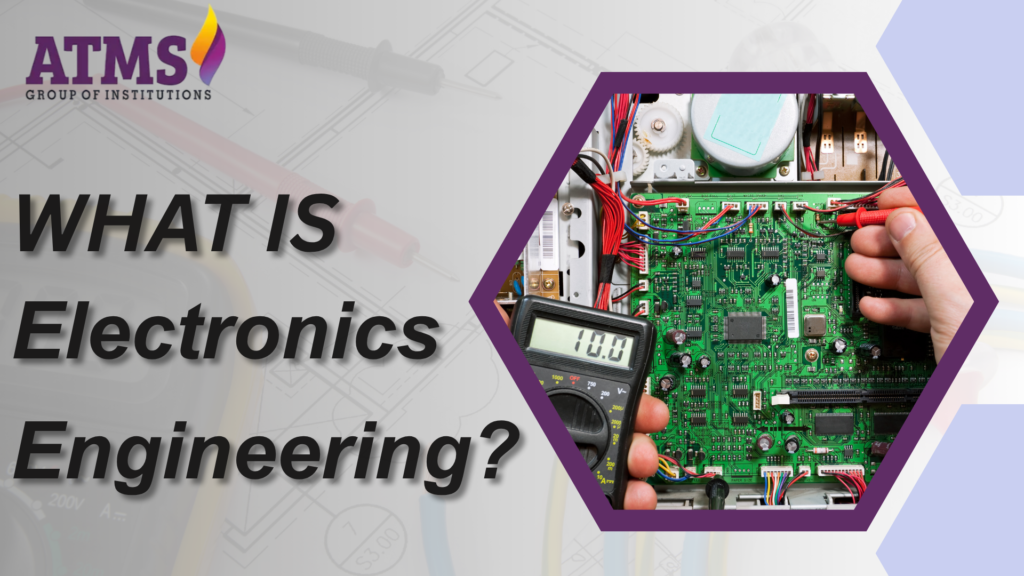
Difference Between Electronics Engineering and Electrical Engineering
While electronics engineering and electrical engineering share foundational principles of engineering, they differ in focus and application.
Comparison
- Extent and Magnitude:
- Electronics Engineering: Focuses on the design and development of miniature electronic components and systems, including microchips and digital circuits.
- Electrical Engineering: Concerns extensive systems such as power generation, transmission, and distribution.
- Domains of Application:
- Electronics Engineering: Fundamental to consumer electronics, computational devices, and digital communications.
- Electrical Engineering: Mainly utilized in infrastructural initiatives, renewable energy, and industrial systems.
- Focus on Technical Aspects:
- Electronics Engineers: Specialize in low-voltage circuitry, signal processing, and semiconductor design.
- Electrical Engineers: Focus on high-voltage systems, power distribution, and control systems.
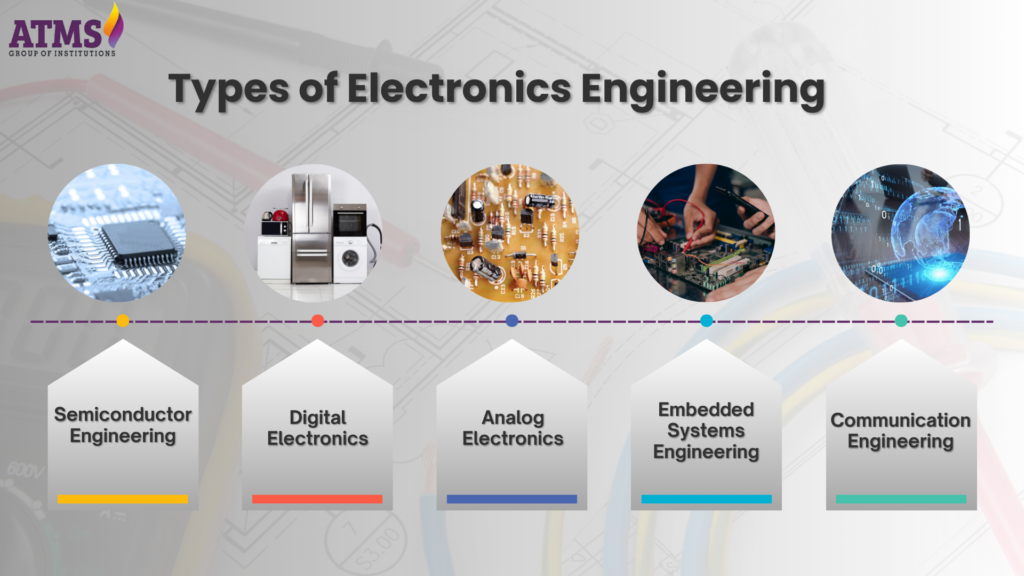
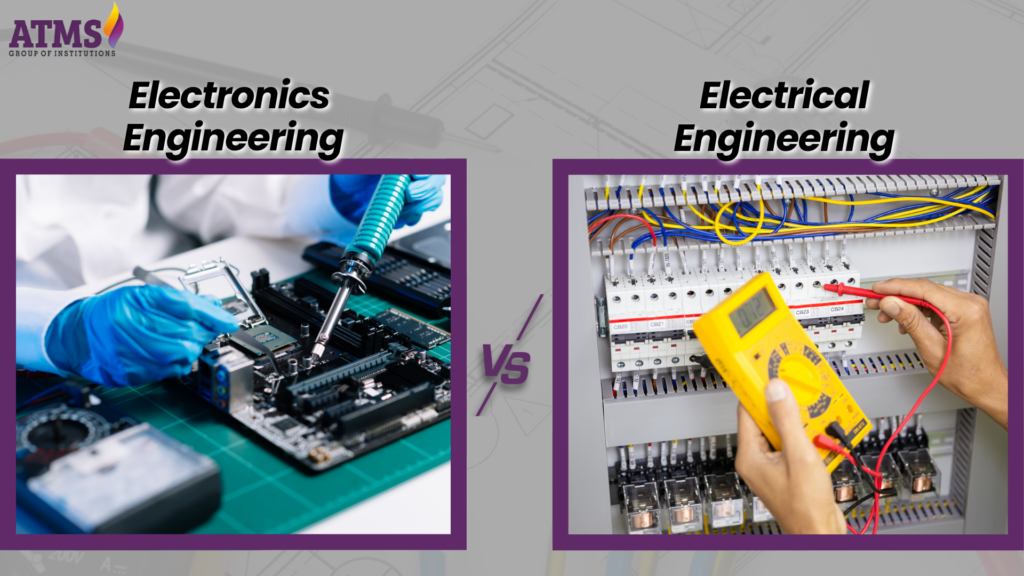
Types of Electronics Engineering
Electronics engineering is a broad field with several specialized branches, each offering unique challenges and career opportunities.
Specializations
- Semiconductor Engineering: Concentrates on the design, manufacture, and evaluation of semiconductor devices that function as the fundamental elements of integrated circuits and microprocessors.
- Digital Electronics: Entails the design of digital circuits that manipulate binary data, encompassing microprocessors, digital signal processors, and memory devices.
- Analog Electronics: Concerns circuits that function with continuous signals. Analog electronics is essential in applications such as audio devices, instrumentation, and sensor technology.
- Embedded Systems Engineering: Integrates hardware and software to create specialized computing systems for applications that span from consumer devices to intricate industrial controls.
- Telecommunication Engineering: Concentrates on the advancement of hardware and methods for data transmission, encompassing wireless communication, fiber optics, and satellite systems.
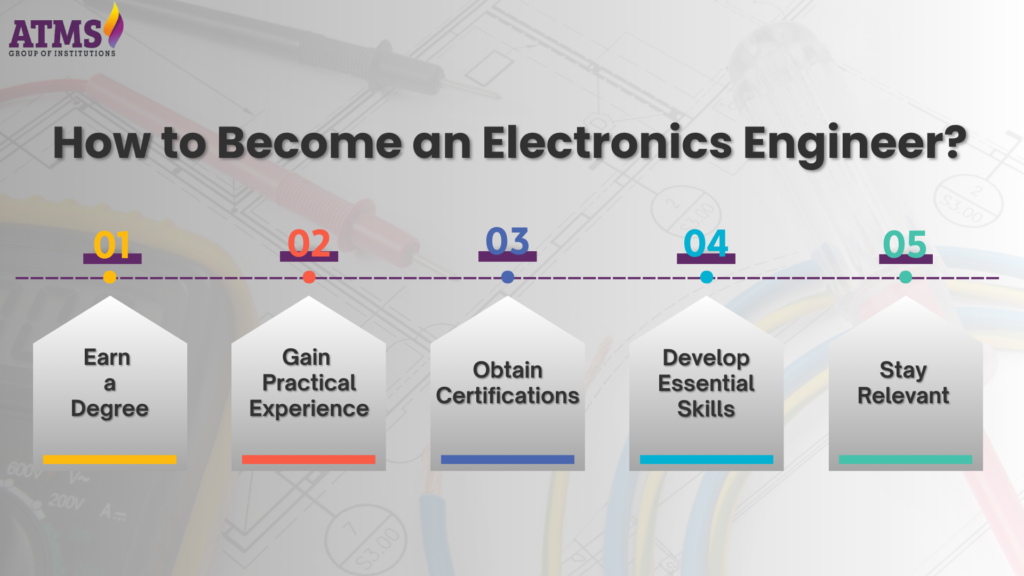
How to Become an Electronics Engineer?
A career in electronics engineering demands both a strong theoretical foundation and practical hands-on experience. Here’s a step-by-step guide to launching your career in this dynamic field.
Steps to Becoming an Electronics Engineer
- Get a degree: Start with a bachelor’s degree in electronics engineering or a related field. Circuit theory, semiconductor physics, and digital systems design are all common subjects in coursework.
- Get real-world experience: Get real-world experience by doing internships, cooperative education programs, and lab projects. When you have practical experience, it’s easier to connect what you know in theory to what you do.
- Get Certifications: Getting specialized training in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) tools can make you more skilled and marketable.
- Gain Basic Skills: Learn how to design circuits, use simulation tools, program (usually in C/C++ or Python), and understand new technologies like IoT and AI integration.
- Stay up to date: Electronics engineering is moving quickly. To stay up to date on the latest trends and breakthroughs, go to workshops, industry conferences, and subscribe to technical magazines.

Electronics Engineering Jobs and Career Opportunities
The electronics engineering sector offers a wide range of exciting career paths, driven by continuous innovation and the growing demand for smarter, more efficient technology.
Career Opportunities
- A semiconductor engineer is an expert in designing and testing semiconductor devices. This job is very important for companies that make microprocessors, memory devices, and other electronic parts.
- Digital Electronics Engineer: This person focuses on designing and improving digital circuits used in computers, phones, and other consumer electronics.
- Systems Engineer: Works on putting together hardware and software into specialized systems. This job is very important in fields like smart home technology, medical devices, and cars.
- Research and Development Engineer: Works with universities or tech companies to help create cutting-edge electronic technologies.
- Communications Engineer: Designs and builds communication systems that let data move between different platforms, such as wireless networks and satellite communications.
In tech giants such as Samsung and Qualcomm, electronics engineers are at the forefront of developing cutting-edge mobile technologies and digital devices, ensuring products meet the demands of modern connectivity and performance.

Future of Electronics Engineering
Electronics engineering is set to shape the future of technology, driven by rapid innovation and the continuous integration of digital and analog systems.
Future Trends
- Miniaturization and Integration: Semiconductor technology is always getting better, which makes it possible to make smaller, more powerful devices. Combining different functions into one chip is a major trend that will change the way products work.
- The growing number of connected devices keeps driving up the need for high-tech electronics. It will be important for electronics engineers to make IoT solutions that are safe, work well, and can grow.
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: The combination of AI and electronics is opening up new possibilities for data processing, automation, and system optimization. The possibilities range from smart sensors to embedded systems that use AI.
- Wearable Technology: As more and more people want to keep track of their health and fitness, electronics engineers are making more advanced wearable devices that are useful, comfortable, and energy-efficient.
- Sustainable Electronics: Because people are becoming more worried about the environment, there is more focus on making electronic devices that use less energy and are better for the environment. This includes new ways to design things that use less power and use materials that are good for the environment.
How ATMS Institute, Hapur Assists Aspiring Engineers
ATMS Institute, Hapur is crucial in cultivating future engineers by offering an optimal blend of theoretical knowledge, practical training, and industrial exposure. The institute equips students to thrive in electronics and electrical engineering, emphasizing innovation and practical application.
Key Highlights:
- Contemporary Infrastructure and facilities: Furnished with state-of-the-art facilities for circuit design, microprocessors, electrical machines, and embedded systems, providing students with practical experience in testing and design.
- Qualified Faculty: A team of proficient and committed educators guarantees that pupils get a profound comprehension of engineering fundamentals while honing their problem-solving and analytical abilities.
- The Electrical Engineering program at ATMS Institute is sanctioned by AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education), ensuring adherence to national quality benchmarks.
- Practical Learning and Workshops: Consistent technical workshops, seminars, and project-oriented learning sessions facilitate students in reconciling theory with practical application.
- Internships and Industry Exposure: Students acquire significant exposure to authentic engineering settings and industry processes through industrial tours and internship programs.
- The institute provides placement aid, soft skills training, and career counseling to equip students for premier employment prospects in the electronics, electrical, and IT sectors.
- ATMS Institute, Hapur, consistently empowers ambitious engineers via quality education, practical skills, and professional preparedness, guaranteeing they are thoroughly equipped to thrive in the swiftly evolving technological landscape.
FAQ Electronic Engineering:
1. What is the main focus of Electronics Engineering?
2. What sets Electrical Engineering apart from Electronics Engineering?
3. Is AICTE’s accreditation for the Electrical Engineering program at the ATMS Institute?
4. What kinds of jobs can you get after studying electronics engineering?
5. Does the ATMS Institute help people find jobs?
Conclusion
Electronics engineering is a field that is always changing and helps modern technology grow. Electronics engineers are at the cutting edge of new ideas, from making semiconductor devices and digital circuits to putting smart systems into everyday life.
There are endless career options in electronics engineering, whether you’re interested in microelectronics, embedded systems, or digital communications. Electronics engineers will continue to be important to making the future smarter and more connected as technology keeps getting better.